
Note: On the KB articles below, the theoretical maximum for 32-bit Windows Server 2003 show up as 470 MB which was true in the Windows 2000 timeframe but no longer correct in Windows Server 2003.Ģ94418 Comparison of 32-bit and 64-bit memory architecture for 64-bit editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003Ĩ88732 Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional 圆4 Edition and of the 圆4-based versions of Windows Server 2003Ĩ89654 How to determine the appropriate page file size for 64-bit versions of Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP What are the theoretical maximums of Paged Pool memory? Here is a nice KB article that shows you the mathematical formula to calculate the kernel memory:Ģ47904 How to Configure the Paged Address Pool and System Page Table Entry Memory Areas

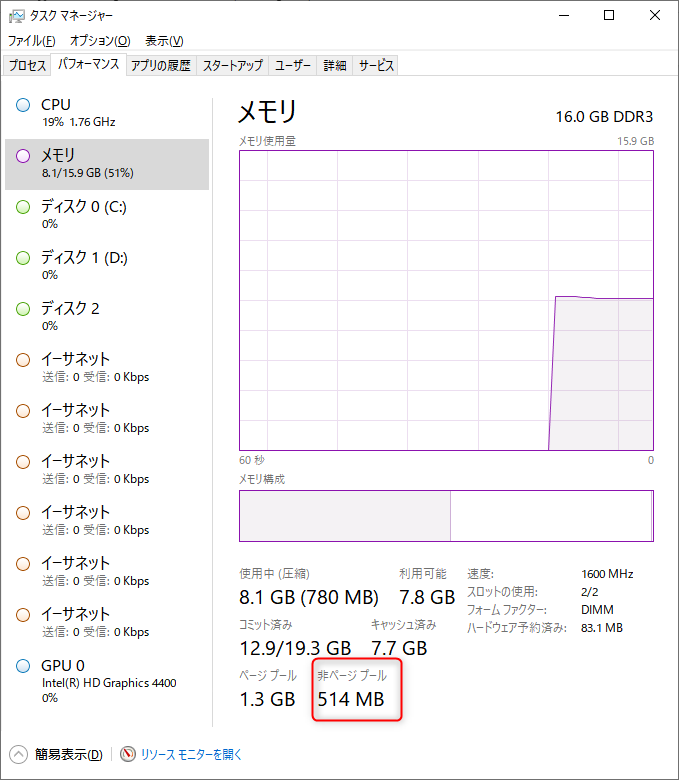
The primary factor that determines the max values is the amount of physical memory the Paged pool memory is a kernel memory that gets calculated during boot time.
#Download poolmon.exe driver
Taking poolmon logs at different time intervals may help you to understand which driver is consuming the paged pool kernel memory. Several factors may deplete the supply of paged pool kernel memory. Your server might become unresponsive and/or hang. You may receive the following error: “Not enough storage available to process this command”. DETAIL – Insufficient system resources exist to complete the requested service.” Your server may stop accepting new user connections and you may receive this message “Windows cannot logon you because the profile cannot be loaded. You might not be able to login to the server via a Remote Desktop (RDP) session. You might not be able to open a network share Otherwise, you will not be flagged about a pool consumption issue.Īdditionally, you might see the following symptoms: This error in the System event log will be only shown if the Server service (srv.sys) detects it. E.E.)ĭescription: The server was unable to allocate from the system paged pool because the pool was empty. There is a nice blog about it by Tate (G.E.S.

Right-click User Defined, select and right-click the and click Stop.Wait for the data to run long enough to capture the information and collect the log while reproducing the issue. Click Add, OK, Next, Next, then select Start this data collector set now, then click Finish.Select Process from the drop-down list, and select from the next drop-down list.Select Memory from the drop-down list and select, then click Add.In the next page from the drop-down list, select Processor, select, and click Add. Under Create data logs, only select Performance counter, and click Next.Type a name (for example, McAfee ), select Create manually, and click OK.Right-click User Defined, select New, and select Data Collector Set.Click Data Collector Sets, User Defined.Type the following command and press ENTER:.

Allocations that have still not been freed, or have continued to increase in size are the likely cause.
#Download poolmon.exe install
Install PoolMon on the computer you want to test, following the Microsoft product instructions.Poolmon.exe is contained in Microsoft Windows Driver Kit (WDK).Type the following command and press ENTER:.Click Start, Run, type cmd, and press ENTER.Enable pool tagging by using the command line:.In the dialog box, enable Enable Pool Tagging.Enable pool tagging by using a dialog box:.If you are using Windows 2003 or later, skip to Step 2. If you are using XP, enable pool tagging as follows.You must enable Gflags.exe to enable pool tagging. Pool tagging is permanently enabled on Windows Server 2003 and later. IMPORTANT: This applies if you want to use PoolMon on Windows XP or earlier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
